- Visibility 167 Views
- Downloads 65 Downloads
- Permissions
- DOI 10.18231/j.jsas.2024.030
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Role of insulin in the management of diabetic foot
- Author Details:
-
Swetha M
-
Ravi Kumar Chittoria *
-
Rashmi V Kumar
Abstract
Introduction: Despite insulin's well-documented benefits in wound healing over the last 70 years, challenges remain regarding the optimal method of administration. While systemic insulin therapy has significant side effects, topical insulin faces challenges with consistent delivery. This study aims to test the hypothesis that local insulin injections can provide sustained high concentrations in wounds, promoting healing with minimal systemic impact, combining the benefits of both systemic and topical insulin therapies.
Aims & Objectives: This study investigates the effect of local insulin injections on wound healing, focusing on enhancing the healing process in a non-healing diabetic foot ulcer. The objective is to determine whether insulin injections at the wound site can accelerate healing by promoting key processes like keratinocyte migration, differentiation, and angiogenesis.
Materials and Methods: Conducted at a tertiary care center in South India, this study involved a 69-year-old male patient with a non-healing ulcer over the lateral aspect of the left foot due to Charcot's joint. The wound area was treated with a mixture of Insulin Isophane and Human Insulin (70/30) in a 4-unit to 10 ml saline ratio per 10 cm². The treatment was followed by a two-layer regenerative scaffold dressing and Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) to support recovery.
Results: The insulin application significantly enhanced wound healing by promoting keratinocyte migration, differentiation, and angiogenesis. These effects led to a noticeable reduction in the time required for wound closure and improved tissue regeneration.
Conclusion: The use of local insulin injections effectively improves wound healing by targeting key processes such as inflammation, re-epithelialization, and angiogenesis. This study underscores the potential of insulin as a promising therapeutic agent for chronic wound management. Further research is recommended to validate these findings and explore its application across diverse wound types.
Introduction
Over 70 years have passed since insulin was recognized as crucial for wound healing.[1] While substantial evidence supports its benefits, no suitable administration method for routine clinical use has been established. Systemic insulin is limited due to significant side effects, while topical insulin struggles with reliable delivery. Research shows varying topical doses, and insulin receptors are found in many tissues, suggesting effective local application could enhance healing if concentrations are maintained.[2] This study tests the hypothesis that local insulin injections can sustain high concentrations in wounds, promoting healing with minimal systemic effects while combining the advantages of systemic and topical approaches.
Case Report
This study was conducted in the Department of Plastic Surgery at a tertiary care centre in South India. The patient was a 69-year-old male with a history of left diabetic foot with Charcot’s joint with a non-healing ulcer over the lateral aspect of left foot.
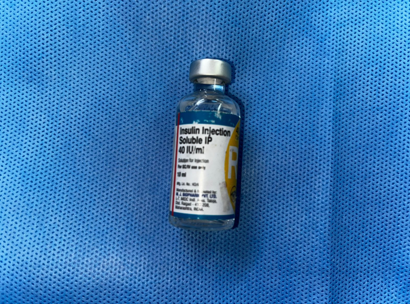
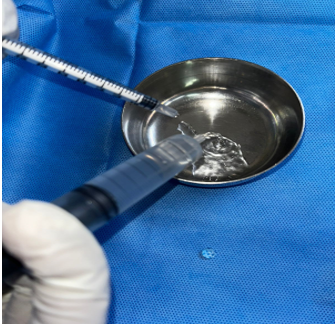
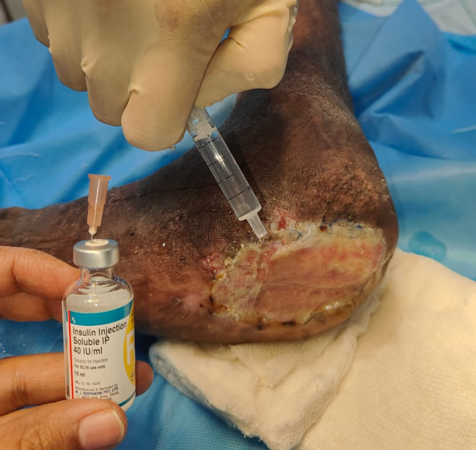
To enhance healing at the donor site, the area was irrigated with a combination of Insulin Isophane and Human Insulin (70/30) in a ratio of 4 units of insulin mixed with 10 ml of 0.9% normal saline per 10 cm² of area. Following this, a two-layer regenerative scaffold dressing was applied, along with Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) to support optimal recovery.
Results
The application of insulin enhances the healing process by promoting keratinocyte migration and differentiation, as well as angiogenesis, ultimately leading to a reduction in healing duration.([Figure 1], [Figure 2], [Figure 3])
Discussion
Wound healing is a complex and dynamic process that involves the reconstruction of cellular structures and tissue layers.[3] It can be divided into three primary stages:
Inflammatory Phase: This initial phase involves the recruitment of blood cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, which help to clear debris and fight infection.
Proliferative Phase: Here, the focus shifts to tissue formation, including the production of extracellular matrix and new blood vessels, leading to the development of granulation tissue.
Remodeling Phase: In this final phase, the newly formed tissue matures and strengthens, improving the integrity of the wound.
Effective wound healing relies on the coordinated action of various proteins, genes, and cellular mediators.[4]
Wound bed preparation, encapsulated by the acronym T.I.M.E[5],, aims to optimize the healing environment for chronic wounds:T: Tissue—assessing and managing non-viable or deficient tissue.I: Infection/Inflammation—addressing and controlling infection.M: Moisture Balance—ensuring an appropriate moisture level in the wound.E: Edge—focusing on the wound edge to promote granulation tissue growth.
Recent literature has highlighted the use of topical insulin as a promising approach in wound bed preparation, potentially enhancing healing outcomes in difficult-to-heal wounds.[6] Topical insulin enhances wound healing by modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses.[7] Research shows that insulin treatment reduces levels of reactive oxygen species, which can have harmful effects on lipids, proteins, and DNA in burn wounds in animal models. [8] Moreover, topical insulin promotes the early recruitment of neutrophils and exerts an anti-inflammatory effect by increasing the number of M2 macrophages and levels of IL-10, aiding in the clearance of dead tissue.[9] In vitro studies demonstrate that insulin enhances macrophage chemotaxis and phagocytosis while regulating the expression of MCP-1 at wound sites.[10] In addition to its effects on inflammation and re-epithelialization, topical insulin promotes keratinocyte migration, accelerates re-epithelialization, and stimulates fibroblast activity.[11] The mechanisms behind insulin-induced keratinocyte migration and differentiation rely on insulin receptors, but also involve epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR), mediated through the PI3K-Akt-Rac1 signalling pathway.[12] Treatment with topical insulin on burned skin has been shown to improve collagen deposition and maturation, indicated by increased levels of hydroxyproline.
Beyond regulating inflammatory and re-epithelialization processes, insulin also promotes angiogenesis in wounds. Topical insulin increases the formation of new blood vessels in healing tissues, and subcutaneous insulin injections have been linked to enhanced migration of microvascular endothelial cells and the formation of endothelial tubes. These effects are associated with the PI3K-Akt-SREBP1 signalling pathway.[13] Additionally, there is increasing evidence that topical insulin has pro-angiogenic effects and aids in vessel maturation in diabetic wounds, likely by restoring impaired insulin signaling pathways, such as PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK, and enhancing the expression of VEGF and angiopoietin-1.[14] Various types of wound dressings are available that facilitate healing through the controlled and sustained release of bioactive insulin, further contributing to the recognition of topical insulin in wound healing. However, additional research is necessary to deepen our understanding of insulin's role in healing different types of wounds. These are limitations of our study.
Conclusion
Topical insulin significantly improves wound healing by targeting inflammation, re-epithelialization, and angiogenesis. As its application in wound management continues to gain recognition, further research is essential to elucidate the mechanisms of action and assess its efficacy across different wound types.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Spampinato S, Caruso G, Pasquale D, Sortino R, Merlo M. The Treatment of Impaired Wound Healing in Diabetes: Looking among Old Drugs. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020;13(4). [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Xu J. Effects of Topical Insulin on Wound Healing: A Review of Animal and Human Evidences. Diab Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:719-27. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H, Hardman M. Wound healing: cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020;10(9). [Google Scholar]
- Schultz G, Chin G, Moldawer L, Fitridge R, MT. . Mechanisms of Vascular Disease: A Reference Book for Vascular Specialists. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz G, Barillo D, Mozingo D, Chin G. Wound Bed Advisory Board Members. Wound bed preparation and a brief history of TIME. Int Wound J. 2004;1(1). [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Xu J. Effects of Topical Insulin on Wound Healing: A Review of Animal and Human Evidences. Diab Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:719-27. [Google Scholar]
- Apolinário P, Zanchetta F, Breder J, Adams G, Consonni S, Gillis R. Anti-inflammatory, procollagen, and wound repair properties of topical insulin gel. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023;56. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Garcialuna J, Berridi K, Bergeron A, Kolosovas-Machuca E, Wang S, Berry G. Local Insulin Improves Wound Healing: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis. Plast Reconstr Surge. 2023;152(6):1114-30. [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y, Fan L, Jiang J. M2 macrophage-polarized anti-inflammatory microneedle patch for accelerating biofilm-infected diabetic wound healing via modulating the insulin pathway. J Nanobiotechnol. 2024;22. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall S, Silva J, Liu Y. Release of insulin from PLGA-alginate dressing stimulates regenerative healing of burn wounds in rats. Clin Sci. 2015;129(12):1115-29. [Google Scholar]
- Yu T, Gao M, Yang P, Pei Q, Liu D, Wang D. Topical insulin accelerates cutaneous wound healing in insulin-resistant diabetic rats. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(10):4682-93. [Google Scholar]
- Chen X, Liu Y, Zhang X. Topical insulin application improves healing by regulating the wound inflammatory response. Wound Repair Regener. 2012;20(3):425-34. [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y, Dhall S, Castro A, Chan A, Alamat R, Martins-Green M. Insulin regulates multiple signaling pathways leading to monocyte/macrophage chemotaxis into the wound tissue. Biol Open. 2018;7(1). [Google Scholar]
- Lima M, Caricilli A, Abreu LD. Topical insulin accelerates wound healing in diabetes by enhancing the AKT and ERK pathways: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. PLoS One. 2012;7(5). [Google Scholar]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
M S, Chittoria RK, Kumar RV. Role of insulin in the management of diabetic foot [Internet]. IP J Surg Allied Sci. 2024 [cited 2025 Nov 06];6(4):131-134. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jsas.2024.030
APA
M, S., Chittoria, R. K., Kumar, R. V. (2024). Role of insulin in the management of diabetic foot. IP J Surg Allied Sci, 6(4), 131-134. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jsas.2024.030
MLA
M, Swetha, Chittoria, Ravi Kumar, Kumar, Rashmi V. "Role of insulin in the management of diabetic foot." IP J Surg Allied Sci, vol. 6, no. 4, 2024, pp. 131-134. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jsas.2024.030
Chicago
M, S., Chittoria, R. K., Kumar, R. V.. "Role of insulin in the management of diabetic foot." IP J Surg Allied Sci 6, no. 4 (2024): 131-134. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jsas.2024.030
